In this guide, you will learn how to set up and build a simple REST API with Spring, that provides CRUD operations for entries that are saved into a database. In addition, you will learn how use JPA’s criteria API to perform filtered searches for records.
Contribute Code
If you would like to become an active contributor to this project please follow theses simple steps:
- Fork it
- Create your feature branch
- Commit your changes
- Push to the branch
- Create new Pull Request
Source code can be downloaded from github.
What you’ll need
- About 30 minutes
- A favorite IDE or Spring Tool Suite™ already install
- JDK 6 or later
Introduction
The JPA Criteria API provides an alternative way for defining dynamic JPA queries. This is very useful for searching/filtering data, where a simple search is not enough.
JPA criteria queries are defined by instantiation of Java objects that represent query elements.
A major advantage of using the criteria API is that errors can be detected earlier, during compilation rather than at runtime.
To show you how the JPA criteria API works, we have created a very simple REST API, with a very simple search functionality for restricting the search results.
For our purposes, lets assume we have a list of authors, and a list of books written by those authors.
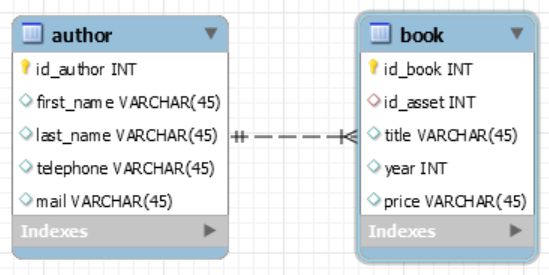
If you would like to know the REST API was built, please refer to our previous article and its related GitHub project.
We will basically focus on the changes introduced in this article and how it uses JPA criteria to filter results.
Author and Books Entity
First, let’s have a look at the Author entities.
@Entity
public class Author {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name = "id_author", unique = true, nullable = false, length = 255)
private Long authorId;
@Column(name = "first_name", nullable = false, length = 60)
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name", nullable = false, length = 60)
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "telephone", nullable = false, length = 60)
private String telephone;
@Column(name = "mail", nullable = false, length = 60)
private String mail;
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "author", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Books> books = new ArrayList<Books>();
public Author() {}
public Author(Long authorId, String firstName, String lastName, String telephone, String mail, List<Books> books) {
this.authorId = authorId;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.telephone = telephone;
this.mail = mail;
this.books = books;
}
//Getters and setters removed for simplicity
}
And now the Books entity.
@Entity
public class Books {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name = "id_book", unique = true, nullable = false, length = 255)
private Long bookId;
@Column(name = "title", nullable = false, length = 60)
private String title;
@Column(name = "year", nullable = false, length = 4)
private Integer year;
@Column(name = "price", nullable = false, length = 10)
private String price;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "id_author", nullable = false)
private Author author;
public Books() {}
public Books(Long bookId, String title, Integer year, String price, Author author) {
this.bookId = bookId;
this.title = title;
this.year = year;
this.price = price;
this.author = author;
}
//Getters and setters removed for simplicity
}
As you may have noticed, we have created the relationship between both entities by adding the annotations @OneToMany and @ManyToOne, and of course the @JoinColumn. Here a brief explanation of each annotation:
@OneToMany: Defines a many-valued association with one-to-many multiplicity.@ManyToOne: Defines a single-valued association to another entity class that has many-to-one multiplicity.@JoinColumn: Specifies a column for joining an entity association or element collection.
Using the CriteriaBuilder
The main factory of the criteria API and all its elements, is the CriteriaBuilder. In other words, the CriteriaBuilder is used to construct criteria queries, compound selections, expressions, predicates, orderings, to mention some.
The CriteriaBuilder interface defines functionality that is specific to top-level queries.
The Root type is the from clause. Please notice that query roots always reference entities.
And finally, we have the Join. A Join to an entity, embeddable, or basic type.
public Page<Author> search(List<SearchCriteria> paramsAuthor, List<SearchCriteria> paramsBooks, Pageable pageable) {
CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder = entityManager.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<Author> criteriaQuery = criteriaBuilder.createQuery(Author.class);
Root<Author> author = criteriaQuery.from(Author.class);
Join<Author, Books> books = author.join("books", JoinType.INNER);
Predicate predicate = this.predicateRootBuilder(criteriaBuilder, paramsAuthor, author);
if(!paramsBooks.isEmpty())
predicate = this.predicateJoinBuilder(criteriaBuilder, paramsBooks, books);
Sort sort = pageable.isPaged() ? pageable.getSort() : Sort.unsorted();
if (sort.isSorted())
criteriaQuery.orderBy(toOrders(sort, author, criteriaBuilder));
criteriaQuery.distinct(true);
criteriaQuery.where(predicate);
TypedQuery<Author> typedQuery = entityManager.createQuery(criteriaQuery);
if(pageable == null)
return new PageImpl<Author>(typedQuery.getResultList());
else {
Long total = (long) typedQuery.getResultList().size();
// Sets the offset position in the result set to start pagination
typedQuery.setFirstResult((int) pageable.getOffset());
// Sets the maximum number of entities that should be included in the page
typedQuery.setMaxResults(pageable.getPageSize());
List<Author> content = total > pageable.getOffset() ? typedQuery.getResultList() : Collections.<Author> emptyList();
return new PageImpl<Author>(content, pageable, total);
}
}
To filter the results, we use a Predicate, which can be a simple or compound predicate: a conjunction or disjunction of restrictions. A simple predicate is considered to be a conjunction with a single conjunct.
The Predicate, uses a very simple class to create the constrains for both, the Author and Books.
public class SearchCriteria {
private String key;
private String operation;
private Object value;
public SearchCriteria() {}
public SearchCriteria(String key, String operation, Object value) {
super();
this.key = key;
this.operation = operation;
this.value = value;
}
//Getters and setters removed for simplicity
}
The SearchCriteria implementation holds our Query parameters:
key: used to hold field name – for example: firstName, age, … etc.operation: used to hold the operation – for example: Equality, less than, … etc.value: used to hold the field value – for example: john, 25, … etc.
The list of Query parameters is filled with SearchCriteria implementations, which are added by the setSearchCriteria function.
private List<SearchCriteria> setSearchCriteria(String search) {
List<SearchCriteria> params = new ArrayList<SearchCriteria>();
if (search != null) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(\\w+?)(:|!:|<|<=|>|>=)(\\w+?),");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(search + ",");
while (matcher.find()) {
params.add(new SearchCriteria(matcher.group(1),
matcher.group(2), matcher.group(3)));
}
}
return params;
}
The Controller
The controller which has suffered most of the changes is this one. You will notice that we have added a pagination feature configured by:
@RequestParam(value = "page", required =false, defaultValue = "0") Integer page: Zero-based page index. Retrieves all rows from a certain offset up.@RequestParam(value = "size", required =false, defaultValue = "10") Integer size: The size of the page to be returned. Limits the number of results returned.@RequestParam(value = "direction", required =false, defaultValue = "asc") String direction: Used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending direction. Direction must not benull.@RequestParam(value = "orderBy", required =false, defaultValue = "authorId") String orderBy: The field name which is used to order the result-set. Properties must not benull.- You may have also noticed, that there are two types of searches:
@RequestParam(value = "searchAuthor", required =false) String searchAuthor: Use for filtering authors based on the author’s properties.@RequestParam(value = "searchBooks", required =false) String searchBooks: Use for filtering authors based on the book’s properties.
Using them is very simple. Just assign the different filter conditions to either or both request parameters, separated by comma. For instance:
http://localhost:8080/author?searchAuthor=firstName:Juan&searchBooks=year:1990
The above example creates two filters. For the author, it only will look for authors which first name iguals “Juan”. While for the books, it will only look for books which publishing year equals “1990”.
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<JsonResponseCreator<AuthorResponse>> search(
@RequestParam(value = "searchAuthor", required = false) String searchAuthor,
@RequestParam(value = "searchBooks", required = false) String searchBooks,
@RequestParam(value = "page", required = false, defaultValue = "0") Integer page, // zero-based page index
@RequestParam(value = "size", required = false, defaultValue = "10") Integer size, // the size of the page to be returned
@RequestParam(value = "direction", required = false, defaultValue = "asc") String direction, // direction must not be {@literal null}
@RequestParam(value = "orderBy", required = false, defaultValue = "authorId") String orderBy // properties must not be {@literal null}
) {
List<SearchCriteria> paramsAuthor = this.setSearchCriteria(searchAuthor);
List<SearchCriteria> paramsBooks = this.setSearchCriteria(searchBooks);
Page<Author> pagedContent = this.authorService.search(paramsAuthor, paramsBooks, PageRequest.of(page, size, Direction.fromString(direction), orderBy));
List<AuthorResponse> response = RestResponseBuilder.createAuthorResponseList(pagedContent.getContent());
JsonResponseCreator<AuthorResponse> jsonResponseCreator = new JsonResponseCreator<AuthorResponse>(pagedContent.getTotalElements(), page, size, direction, orderBy, response);
return new ResponseEntity<JsonResponseCreator<AuthorResponse>>(jsonResponseCreator, HttpStatus.OK);
}
Conclusion
The presented implementation of REST API is simple, but yet very powerful due to its search feature. Of course, there is still room for improvements (which will be implemented in future articles), but it will give you a solid starting point.
The full implementation of this article can be found in the GitHub project – this is a Maven-based project, so it should be easy to import and run as it is.